All you need to know about living the Bold life
Bold is a Misters proprietary blend capsule of 100% natural herbal ingredients containing 18 Ayurvedic herbs consisting of Gokshura, Shilajit, Ashwagandha and more that have a positive influence on male function for a more satisfying love life proving helpful for conditions like Erectile Dysfunction (ED). Frequently asked questions (FAQ’s) regarding this capsule such as its effects, how it functions, it’s constituents and why you should choose it are answered below.
What is Erectile Dysfunction / ED?
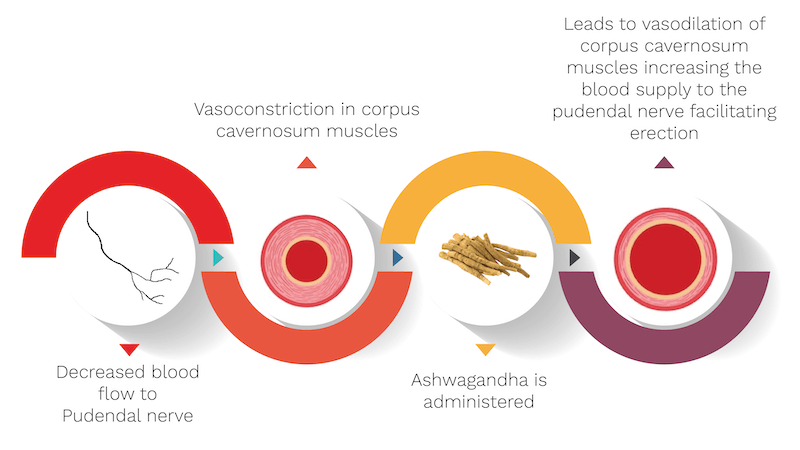
Due to reduced blood supply to the penis, vasoconstriction or narrowing of blood vessels occurs, further causing decreased blood supply which then leads to erectile dysfunction (ED). It refers to an inability to obtain and maintain penile erection.
What are some common causes of ED?
It is usually the result of androgen deficiency in aging men, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, spinal cord injury, high level of cholesterol, hypertension, prostate surgery, prostate and heart disease, penis anatomical deformity, social and psychological conditions like unhappy marital relationships, depression and stress.
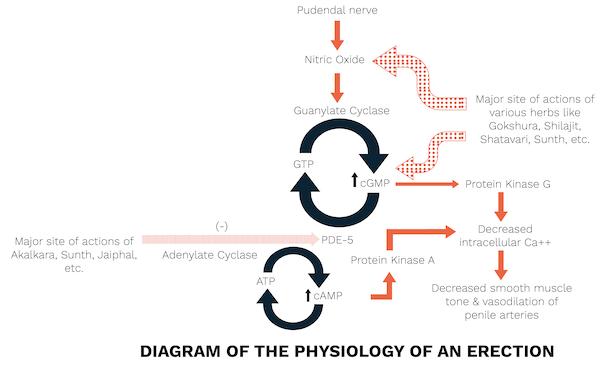
Why choose Bold for Erectile Dysfunction?
The use of allopathic drugs have various side-effects that limit their usage; hence, Misters considers it more prudent to turn towards alternative options utilising traditional systems of medicine that include medicinal plants with fewer or no recorded side-effects, employing herbal medications to manage sexual dysfunctions. Bold consists of ingredients which work synergistically, enhancing and elevating male sexual potency.
What are Bold’s primary ingredients and their mechanisms?
The formulation of Bold is a proprietary blend of 18 herbal ingredients that include Ashwagandha, Shilajit, Gokshura, Shatavari, Mastaki, Kesar, Jaiphal, Vidarikand, Akalkara, Tejpatra and more… Learn about them below:
What are the mechanisms of Ashwagandha?
It’s biological source is Withania somnifera, belonging to the Solanaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 50 mg.
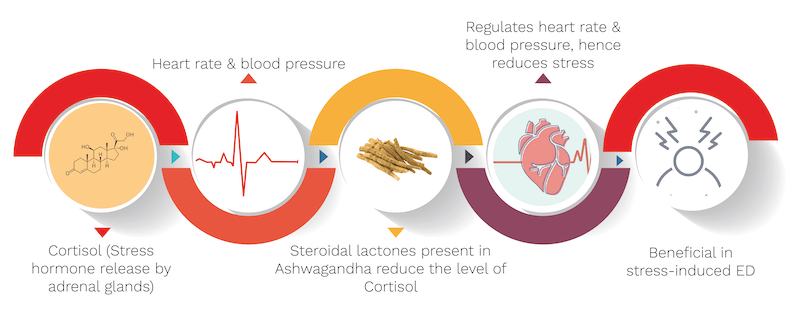
Ashwagandha consists of steroidal lactones such as Withaferin, Withanolide D & Withanone which work based on 4 major mechanisms to treat erectile dysfunction which are explained with the help of informative diagrams below.
Mechanism 2:
Mechanism 3:
Mechanism 4:
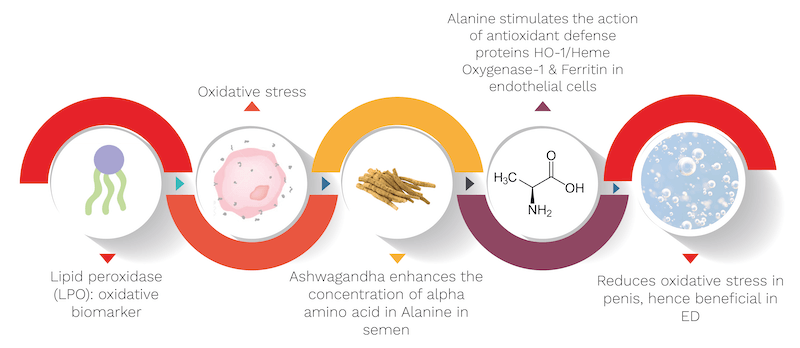
What is Ashwagandha’s effect in combination with other herbs?
- Dactylorhiza maculata (dried root and tubers): increases libido, improves erection, delays ejaculation, increases testosterone, semen volume & spermatogenesis.
- Crocus sativus (stigma): improves Rigiscan parameters (rigidity & tumescence) and sexual parameters such as erectile function and overall satisfaction.
- Ginseng: improves erectile parameters such as penile rigidity, girth, erection duration, and libido.
- Tribulus terrestris: improves semen parameters, including liquefaction time.
- Sida cordifolia, Shilajit: Enhance sperm production.
- Mucuna pruriens: Improves steroidogenesis thereby having a positive effect on semen quality.
What are some secondary effects of Ashwagandha?
By studying the properties of Ashwagandha individually and in combination with other ingredients, it was inferred that it improves the overall sexual health of men, having a positive influence on erectile function. However, it imparts secondary effects as well which indirectly help to improve this condition.
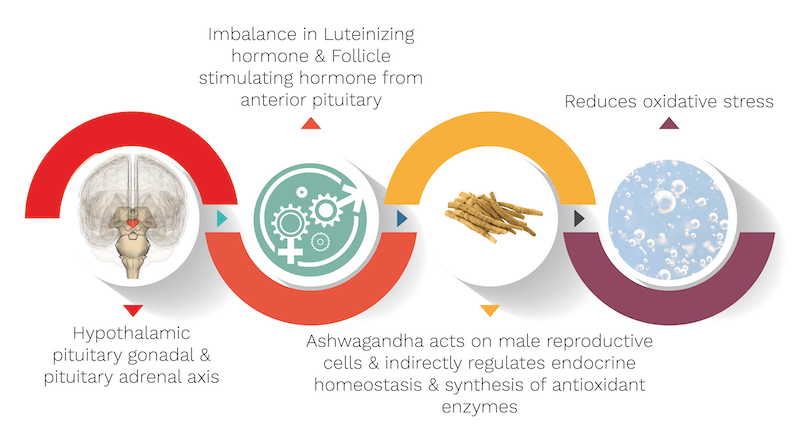
Since Androgens or sexual hormones are dependent on the quality of semen, also testosterone, the primary sex hormone in males plays a vital role in sexual drive and libido stimulation. Ashwagandha acts by improving overall sexual health by targeting various hormones. It enhances the level of testosterone & Luteinizing hormone (LH), enhancing spermatogenesis and sexual drive. It also decreases the level of Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) & Prolactin (Prl) which in turn normalises hormonal levels, leading to a healthier life.
What are the mechanisms of Gokshura?
It’s biological source is Tribulus terrestris, belonging to the Zygophyllaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 50 mg. Gokshura’s mechanism is explained with the help of an informative diagram below.
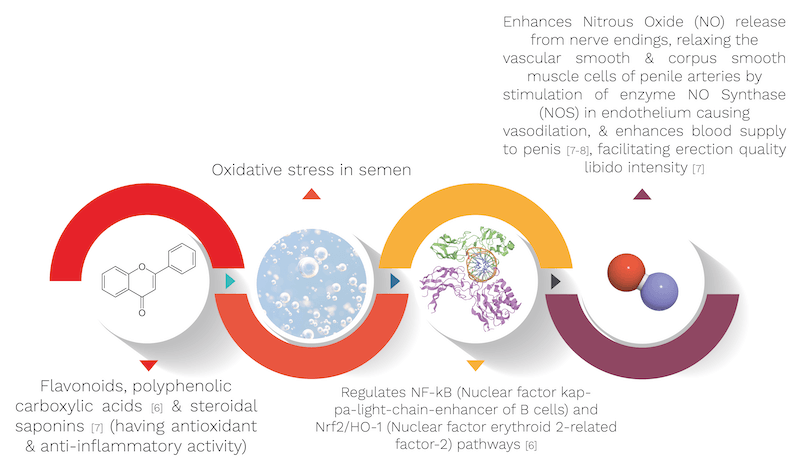
- Nitric oxide mediates the formation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP); this mechanism could promote erection by vasodilation and increased blood supply to the corpora cavernosa.
- Oxidative stress causes reactive oxygen species and advanced end glycation products to react with nitric oxide in the vasculature, forming reactive nitrogen species that contribute to the pathogenesis of erectile dysfunction.
- Due to its presence of saponins & tannins, it increased activity in randomised controlled trials.
What is Gokshura’s effect in combination with other herbs?
It has synergistic effect in combination with Ashwagandha & Mucuna pruriens.
What are some secondary effects of Gokshura?
- Antioxidant activity
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antidiabetic activity
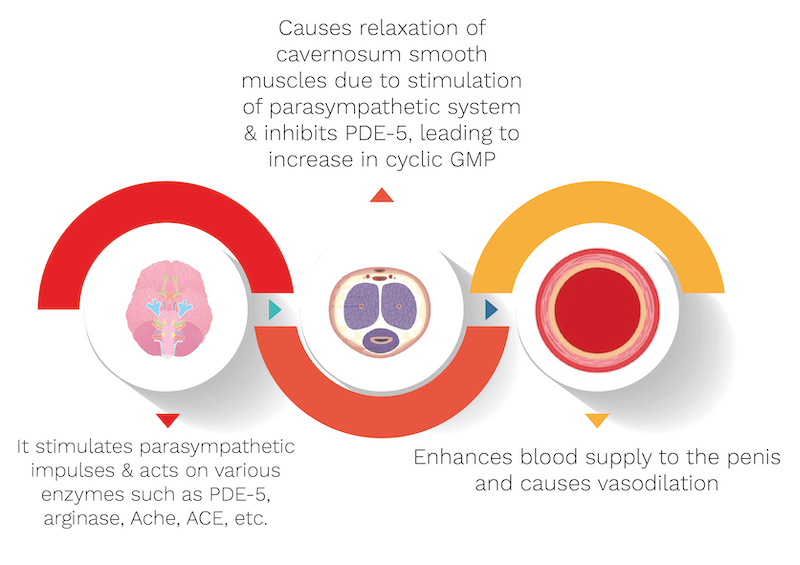
What are the mechanisms of Shilajit?
It’s biological source is Euphorbia royleana, belonging to the Euphorbiaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 50 mg. Shilajit’s mechanism is explained with the help of an informative diagram below.
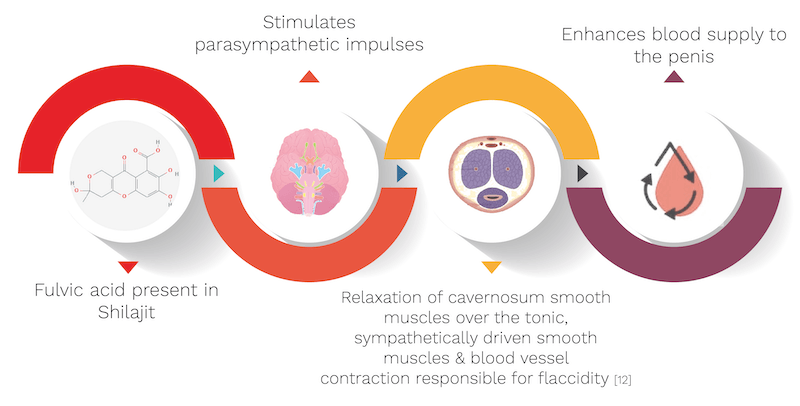
- It stimulates parasympathetic impulses resulting in enhanced blood supply to the reproductive organ culminating in a sustained erection.
What are the mechanisms of Shatavari?
It’s biological source is Asparagus racemosus, belonging to the Asparagaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 20 mg. Shatavari’s mechanism is explained with the help of an informative diagram below.
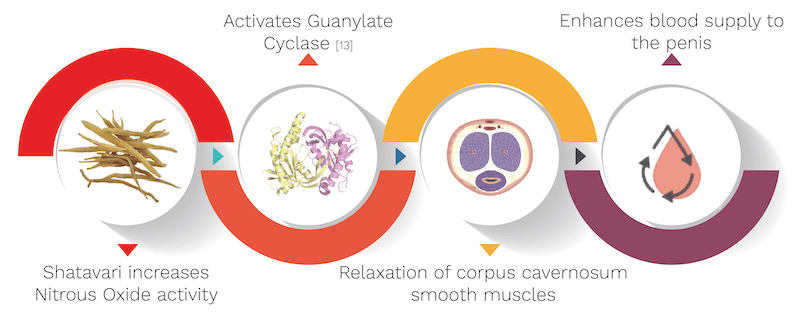
- Increases the NO activity leading to activation of Guanylate cyclase producing penile erection.
What are some secondary effects of Shatavari?
- Increases sperm count.
What are the mechanisms of Mastaki?
It’s biological source is Pistacia lentiscus, belonging to the Anacardiaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg. Mastaki’s mechanism is explained with the help of an informative diagram below.
- The resin ‘mastic’ present in Mastaki proves to be a natural supplement of zinc which is an essential element to maintain overall reproductive health among men.
- It promotes healthy prostate function and is important for proper maintenance of male reproductive systems. It also supports synthesis of testosterone and other male hormones which improve libido and hence indirectly facilitate proper erectile functioning.
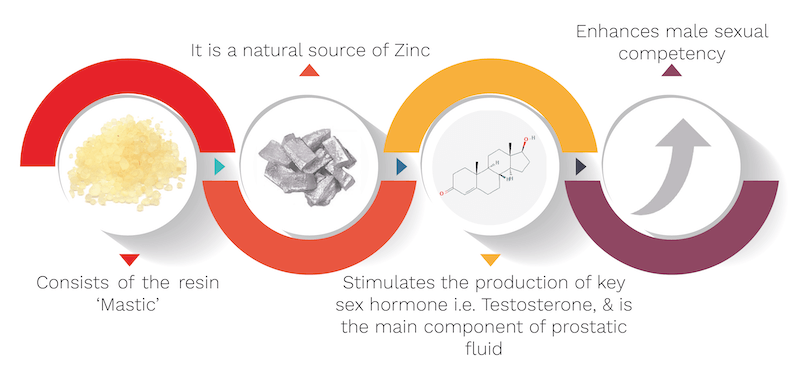
What are some secondary effects of Mastaki?
- It acts as an aphrodisiac and maintains hormonal balance.
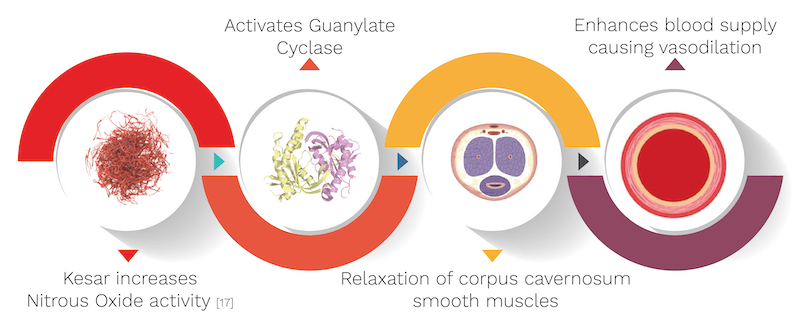
What are the mechanisms of Kesar?
It’s biological source is Crocus sativus, belonging to the Iridaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg. Kesar’s mechanism is explained with the help of an informative diagram below.
- The NPT (Nocturnal penile tumescence) test and International index of erectile function IIEF-15 parameters were improved in stress-induced erectile dysfunction.
- Rigiscan parameters are also improved leading to enhanced rigidity & tumescence.
- Results in significantly greater improvement in erectile function and intercourse satisfaction domains.
- Saffron interacts with both nitric oxide and opioid systems playing a noteworthy role in erectile function.
What is Kesar’s effect in combination with other herbs?
- Tribulus terrestris: Positive effect on semen parameters in terms of sperm motility in men suffering from idiopathic infertility.
What are some secondary effects of Kesar?
- Anti-inflammatory
- Radical-scavenging
- Neuro-protective
What are the mechanisms of Jaiphal?
It’s biological source is Myristica fragrans, belonging to the Myristicaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg. Jaiphal’s mechanism is explained with the help of an informative diagram below.
- It had nerve stimulating properties leading to significant increase in the Mounting Frequency, Intromission Frequency, and Intromission Latency and caused significant reduction in the Mounting Latency and Post Ejaculatory Interval. It also significantly increases Mounting Frequency with penile anaesthetisation as well as Erections, Quick Flips, Long Flips and the aggregate of penile reflexes with penile stimulation.
- Invitro study shows inhibitory potential of Nutmeg extracts on PDE-5(phosphodiesterase-5), arginase, AchE (Acetylcholine esterase, ACE (Angiotensin converting enzyme) activities, and metal-induced penile damage. The phenolic constituents of the extracts may contribute to their enzyme inhibitory and antioxidant activities. Nutmeg had significantly high levels of caffeic acid, gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, rutin, quercetin, quercitrin and kaempferol. The high phenolic and flavonoid content in nutmeg extract correlates with its higher inhibitory effects on metal-induced lipid peroxidation and enzymes linked to ED.
- Inhibits Rho-kinase 2 (ROCK-II) enzyme producing a positive influence on erectile function.
What are some secondary effects of Jaiphal?
- Antioxidant effect
What is Jaiphal’s effect in combination with other herbs?
- Synergistic effect with drumstick in management of erectile dysfunction.
What are the mechanisms of Vidarikand?
It’s biological source is Pueraria tuberosa, belonging to the Fabaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10mg. Vidarikand’s mechanism is explained with the help of an informative diagram below.
- Improves androgenesis and sexual behaviour via FSH LH cascade.
- Reduces the mount latency and post ejaculation latency with a 3/4th increase in the mount frequency.
- It contains Tuberosin which acts as an Antioxidant. By this property of Tuberosin it secretes the Nitric oxide in penile tissue. Nitric oxide is a chemical compound that plays a major role in male sexual function. An abundance of nitric oxide can improve circulation and lead to more frequent erections. The inner-lining of blood vessels use nitric oxide to signal the surrounding smooth muscle to relax. This leads to vasodilation (blood vessel dilation), and a consequently increased blood flow. Even increased blood flow can lead to more frequent erections.
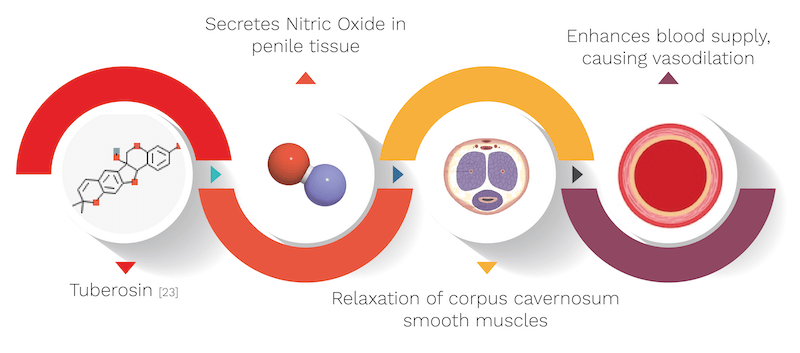
What are some secondary effects of Vidarikand?
- Increases serum concentration of FSH and also improves serum testosterone level.
- Increases the weights of the testis, epididymis, and seminal vesicles and spermatogenesis.
- Vidarikanda has antioxidant activity, neuroprotective, antidepressant and anxiolytic activity(due to Diazein, Puerarin, and Genistein).
- Puerarin also have the Antimicrobial property.
- It also contains beta-Sitosterol and Stigmasterol which acts as Androgenic and Hypolipidemic effects respectively.
- Vidarikanda contains Steroid saponin (diosgenin) which reduces the level of serum cholesterol.
What are the mechanisms of Akalkara?
It’s biological source is Anacyclus pyrethrum, belonging to the Asteraceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg. Akalkara’s mechanism is explained with the help of an informative diagram below.
- Increases the penile erection, similar to the increase in penile erection index (PEI) observed by administration of testosterone. The erection was observed due to NO based intervention.

- It causes considerable elevation in average sperm count in Vas deferens & Epididymis.
- Resin compound called pyrethrin or pellitorin leads to improvement in ED.
What are some secondary effects of Akalkara?
- Stimulates the level of testosterone and favours spermatogenesis causing increased blood flow and growth of target tissues.
What are the mechanisms of Tejpatra?
It’s biological source is Cinnamomum tamala, belonging to the Lauraceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg. Tejpatra’s mechanism is as follows:
- It acts on ROS species, thereby protecting against oxidative stress.
What are some secondary effects of Tejpatra?
- Anti-inflammatory activity.
What are the mechanisms of Lavang?
It’s biological source is Syzygium aromaticum, belonging to the Myrtaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg. Lavang’s mechanism is explained with the help of an informative diagram below.
- Activation of Rho-kinase 2 (ROCK-II) results in contraction of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle and by inhibiting this enzyme, relaxation in corpus cavernosum smooth muscles is observed in vitro and in vivo hence, clove, which has inhibitory effect on this enzyme is useful in management of erectile dysfunction (ED).
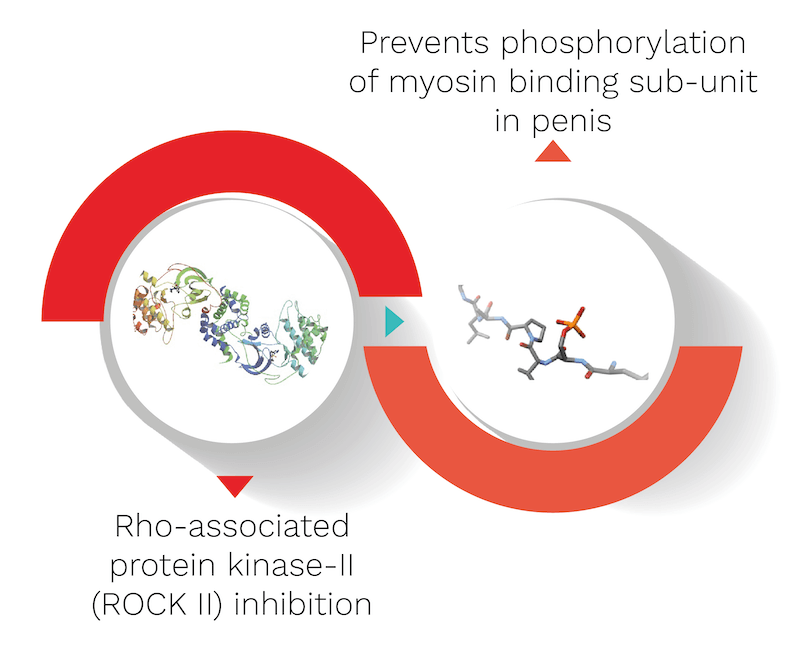
What are some secondary effects of Lavang?
- Antioxidant activity
What are the mechanisms of Sunth?
It’s biological source is Zingiber officinalis, belonging to the Zingiberaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg. Sunth’s mechanism is as follows.
- It has cGMP-PDEI effect, i.e. it acts by inhibiting the Phosphodiesterase (PDE) enzyme thereby preventing the muscles in the penis from contracting, leading to vasodilation.
What is Sunth’s effect in combination with other herbs?
- Synergistic effect with Tribulus terrestris.
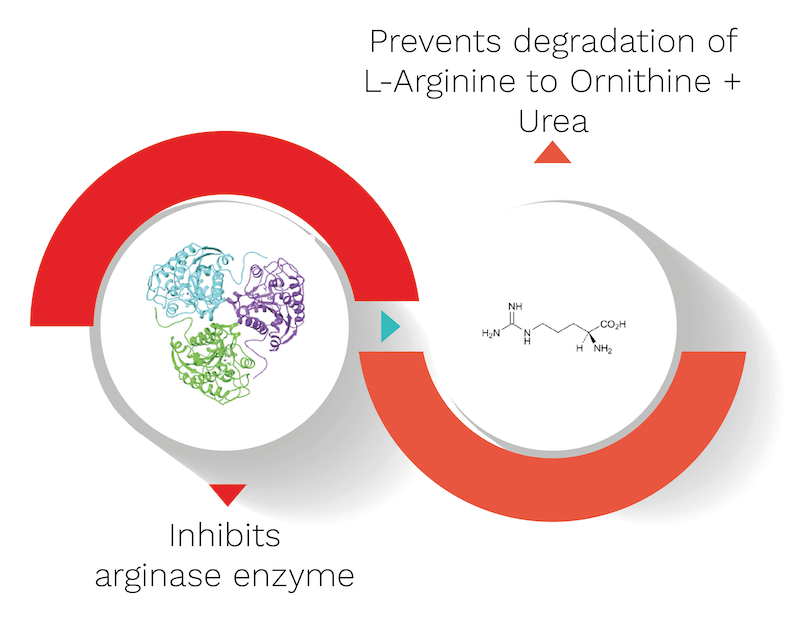
What are the mechanisms of Taj?
It’s biological source is Cinnamomum cassia, belonging to the Lauraceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg. Taj’s mechanism is explained with the help of an informative diagram below.
Why Misters?
Scientific products
Discreet doorstep delivery
Full privacy guaranteed
Trusted by over 25,000 Indian Men
Judgement free zone
Backed by leading doctors
What are Bold’s secondary ingredients and their mechanisms?
Some secondary ingredients used in the formulation of the Bold capsule Amla, Piplamool, Kabachini and more. Learn about them below:
What are the mechanisms of Amla?
It’s biological source is Emblica officinalis, belonging to the Euphorbiaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 200 mg. Amla’s mechanisms are as follows.
- It is helpful in improvement of various semen parameters such as semen volume, motility, sperm count, live normal spermatozoa & reduction of live abnormal sperm percentage which combats the inability to maintain erection.
- It is also hepatoprotective in nature. It increases the production of ATP, which indirectly favours spermatogenesis thereby boosting the overall male reproductive response.
- It is ameliorative in nature. Acts as an adjuvant due to presence of certain bioactive compounds including emblicanin A, emblicanin B, punigluconin & pedunculagin which are known to provide protection against free radicals combating oxidative stress.
- It also enhances viability (increase in the number of live sperm).
What are the mechanisms of Piplamool?
It’s biological Source is Piper longum, belonging to the Piperaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg. Amla’s mechanisms are as follows.
- Acts as bioenhancer i.e. improves the overall efficacy of the formulation due to presence of piperine.
- Used in Vajikarana therapy to treat various sexual disorders (No scientific claim).
What are some therapeutic ingredients that are scientifically unclaimed but are mentioned in ancient texts?
There are 3 ingredients used in this formulation which are mentioned in the ancient texts such as Ayurveda and Unani system of medicine as Vajikarana & hot temperament herbs but no scientific claims could be established for these herbs.
- Kababchini: It’s biological Source is Piper cubeba, belonging to the Piperaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg.
- Elcha: It’s biological Source is Amomum subulatum, belonging to the Zingiberaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg.
- Nirbhishi: It’s biological Source is Delphinium denudatum, belonging to the Ranunculaceae family. It’s quantity used in the capsule is 10 mg.
How about some parting thoughts?
Herbal remedies are efficient in the management of ED since historical times. In this product, all the herbal components that are used possess significant pharmacological activity which is scientifically verified and effective in reversing the problem of erectile dysfunction by acting on various levels. The ingredients such as Gokshura, Shilajit & Shatavari act by enhancing the nitrous oxide (NO) production, facilitating vasodilation. Sunth acts by targeting cGMP stimulation & PDE-5 inhibition, thereby causing relaxation of smooth muscles, leading to an erection. Other major ingredients including Jayphal & Akalkara enhance PEI & sperm count. All the ingredients present in this formulation work synergistically to improve the condition of erectile dysfunction, giving men a chance to lead more satisfying and fulfilling lives.
REFERENCES
- Goel B, Maurya NK. Aphrodisiac Herbal therapy for Erectile Dysfunction. Archives of Pharmacy Practice. 2020 Jan 1;11(1).
- Pathak M, Sharma S, Kushwaha PP, Kumar S. Functional lead compounds and targets for the development of drugs for the treatment of male infertility. InPhytochemicals as Lead Compounds for New Drug Discovery 2020 Jan 1 (pp. 333-345). Elsevier.
- Mandlik DS, Namdeo AG. Pharmacological evaluation of Ashwagandha highlighting its healthcare claims, safety, and toxicity aspects. Journal of Dietary Supplements. 2020 Apr 2:1-44.
- Verma P. International Journal of Gynaecology Research. Successive lowering of LPO, control proportion of ROS and recovered seminal plasma activity.
- Jha K, Acharya L. Ayurvedic Management of Oligospermia (Ksheenshukra): A case report. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrated Medical Sciences (ISSN 2456-3110). 2020 May 25;5(2):239-43.
- Meena P, Anand A, Kumar V. A comprehensive overview of Gokshura (Tribulus terrestris Linn.). Journal of Ayurveda and Integrated Medical Sciences (ISSN 2456-3110). 2020 Feb 5;4(6):205-11.
- Ștefănescu R, Tero-Vescan A, Negroiu A, Aurică E, Vari CE. A Comprehensive Review of the Phytochemical, Pharmacological, and Toxicological Properties of Tribulus terrestris L. Biomolecules. 2020 May;10(5):752.
- Kam SC, Do JM, Choi JH, Jeon BT, Roh GS, Hyun JS. In vivo and in vitro animal investigation of the effect of a mixture of herbal extracts from Tribulus terrestris and Cornus officinalis on penile erection. The journal of sexual medicine. 2012 Oct 1;9(10):2544-51.
- Phillips OA, Mathew KT, Oriowo MA. Antihypertensive and vasodilator effects of methanolic and aqueous extracts of Tribulus terrestris in rats. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2006 Apr 6;104(3):351-5.
- Malavige LS, Levy JC. Erectile dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. The journal of sexual medicine. 2009 May 1;6(5):1232-47.
- Srivatsav A, Balasubramanian A, Pathak UI, Rivera-Mirabal J, Thirumavalavan N, Hotaling JM, Lipshultz LI, Pastuszak AW. Efficacy and safety of common ingredients in aphrodisiacs used for erectile dysfunction: a review. Sexual medicine reviews. 2020 Mar 2.
- Jha K, Acharya L. Ayurvedic Management of Oligospermia (Ksheenshukra): A case report. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrated Medical Sciences (ISSN 2456-3110). 2020 May 25;5(2):239-43.
- Abarikwu SO, Onuah CL, Singh SK. Plants in the management of male infertility. Andrologia. 2020 Apr;52(3):e13509
- Sawidis T, Yurukova L, Askitis T. Chios mastic, a natural supplement for zinc to enhance male sexuality and prostate function. Pharmaceutical biology. 2010 Jan 1;48(1):48-54.
- Shamsa A, Hosseinzadeh H, Molaei M, Shakeri MT, Rajabi O. Evaluation of Crocus sativus L.(saffron) on male erectile dysfunction: a pilot study. Phytomedicine. 2009 Aug 1;16(8):690-3.
- Modabbernia A, Sohrabi H, Nasehi AA, Raisi F, Saroukhani S, Jamshidi A, Tabrizi M, Ashrafi M, Akhondzadeh S. Effect of saffron on fluoxetine-induced sexual impairment in men: randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Psychopharmacology. 2012 Oct 1;223(4):381-8.
- Maleki-saghooni N, Mirzaeii K, Hosseinzadeh H, Sadeghi R, Irani M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials on saffron (Crocus sativus) effectiveness and safety on erectile dysfunction and semen parameters. Avicenna journal of phytomedicine. 2018 May;8(3):198.
- Hosseinzadeh H, Nassiri‐Asl M. Avicenna's (Ibn Sina) the Canon of Medicine and saffron (Crocus sativus): a review. Phytotherapy Research. 2013 Apr;27(4):475-83.
- Ahmad S, Latif A, Qasmi IA, Amin KM. An experimental study of sexual function improving effect of Myristica fragrans Houtt.(nutmeg). BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2005 Dec 1;5(1):16.
- Odubanjo VO, Olasehinde TA, Oyeleye SI, Oboh G, Boligon AA. Seed extracts from Myristica fragrans (Nutmeg) and Moringa oleifera (Drumstick tree) inhibits enzymes relevant to erectile dysfunction and metal‐induced oxidative damage in rats' penile tissues. Journal of Food Biochemistry. 2018 Feb;42(1):e12452.
- Goswami SK, Kumar PM, Jamwal R, Dethe S, Agarwal A, Naseeruddin IM. Screening for Rho-kinase 2 inhibitory potential of Indian medicinal plants used in management of erectile dysfunction. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2012 Dec 18;144(3):483-9.
- Chauhan NS, Sharma V, Thakur M, Christine Helena Frankland Sawaya A, Dixit VK. Pueraria tuberosa DC extract improves androgenesis and sexual behaviour via FSH LH cascade. The Scientific World Journal. 2013;2013.
- Katti A, Malipatil N, Reddy S. EFFICACY OF VIDARIKANDA (PUERARIA TUBEROSE) CHURNA IN KLAIBYA (ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION): A DOUBLE BLIND, PLACEBO CONTROLLED, CLINICAL TRIAL.
- Sharma V, Thakur M, Chauhan NS, Dixit VK. Evaluation of the anabolic, aphrodisiac and reproductive activity of Anacyclus pyrethrum DC in male rats. Scientia pharmaceutica. 2009 Mar;77(1):97-110.
- Shahraki MR. The Effects of Aqueous Extract of Anacyclus pyrethrum on sperm count and reproductive organs in adult male rats.
- Shahraki S, Rad JS, Rostami FM, Shahraki MR, Arab MR. Effects of aqueous root extracts of Anacyclus Pyrethrum on gonadotropins and testosterone serum in adult male rats. American Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Therapeutics. 2014;2(6):767-72.
- Gill S, Panthari P, Kharkwal H. Phytochemical investigation of high altitude medicinal plants Cinnamomum tamala (Buch-ham) Nees and Eberm and Rhododendron arboreum smith. Am J Phytomed Clin Ther. 2015;3:512-28
- Panthari P, Kharkwal H. Phytochemical investigation of high altitude medicinal plants Cinnamomum tamala (Buch-ham) Nees and Eberm and Rhododendron arboreum smith. Am J Phytomed Clin Ther. 2015;3:512-28.
- Goswami SK, Kumar PM, Jamwal R, Dethe S, Agarwal A, Naseeruddin IM. Screening for Rho-kinase 2 inhibitory potential of Indian medicinal plants used in management of erectile dysfunction. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2012 Dec 18;144(3):483-9.
- Khanavi M, Azimi H, Ghiasi S, Hassani S, Rahimi R, Nikfar S, Ajani Y, Shams-Ardekani MR, Abdollahi M. Specifying human platelet cAMP and cGMP phosphodiesterase inhibitory activity of the plants used in traditional Iranian medicine for the purpose of erectile dysfunction. Int J Pharmacol. 2012 Apr 1;8(3):161-8.
- Kanagaraju P, Churchill RR, Veeramani P, Rathnapraba S. Effect of Amla Extract on Semen Quality of Layer Breeder Cocks.
- Dutta AL, Sahu CR. Protective effect of Emblica officinalis on chlorpyrifos (an organophosphate insecticide) induced male reproductive system in rats. Int J Pharm Biosci 2013b. 2013;4:49-58.
- Jaafar MS, Banana HJ. Effect of adding different levels of amla fruit extract and vitamin C to tris-based extender in the semen properties preserved at 5◦C of awassi rams.
- Tatiraju DV, Bagade VB, Karambelkar PJ, Jadhav VM, Kadam V. Natural bioenhancers: An overview. J Pharmacogn Phytochem. 2013;2(3):55-60.
- Dalal PK, Tripathi A, Gupta SK. Vajikarana: Treatment of sexual dysfunctions based on Indian concepts. Indian journal of psychiatry. 2013 Jan;55(Suppl 2):S273.
- Goswami SK, Inamdar MN, Jamwal R, Dethe S. Effect of Cinnamomum cassia methanol extract and sildenafil on arginase and sexual function of young male Wistar rats. The journal of sexual medicine. 2014 Jun 1;11(6):1475-83.
- Goswami SK, Inamdar MN, Jamwal R, Dethe S. Effect of Cinnamomum cassia methanol extract and sildenafil on arginase and sexual function of young male Wistar rats. The journal of sexual medicine. 2014 Jun 1;11(6):1475-83.
